This paper focuses on two phenomena in Irish agreement – namely, complementarity between overt in-situ arguments and agreement, and the obviation of this complementarity under A-movement. An analysis of these facts is offered in terms of the defective goal ‘incorporation’ (DGI) mechanism proposed by Roberts (2010), and applied to cases of complementarity in Bantu languages by Iorio (2014), and van der Wal (2015, 2020, 2022), as well as asymmetric chains under A-movement, consisting of a full copy and a pronominal 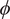 $ \phi $-feature bundle; cf. similar configurations discussed by Takahashi & Hulsey (2009), Harizanov (2014), Kramer (2014), Baker & Kramer (2018), inter alios. It is shown that this approach accounts for the facts in Irish and that the same account can be extended to explain facts concerning participial agreement in, for example, Italian. Additional cross-linguistic implications are also considered, particularly with respect to French and Welsh.
$ \phi $-feature bundle; cf. similar configurations discussed by Takahashi & Hulsey (2009), Harizanov (2014), Kramer (2014), Baker & Kramer (2018), inter alios. It is shown that this approach accounts for the facts in Irish and that the same account can be extended to explain facts concerning participial agreement in, for example, Italian. Additional cross-linguistic implications are also considered, particularly with respect to French and Welsh.